How to improve coverage for 5G mmWave
Not all 5G is created equal. 5G low-band operates at 600-2200 MHz, 5G mid-band at 2.5/3.5 GHz, and 5G high-band at 24-40 GHz. Low band is excellent for wireless coverage but doesn’t deliver much bandwidth. High-band (also known as mmWave, or millimeter wave) may deliver blazingly fast broadband, but a cell tower typically only covers a few hundred meters. Mid-band sits in between, striking a balance between coverage and bandwidth.
The appetite for ever-higher speeds continues unabated, so there’s been much activity around 5G mmWave. Operators have launched or are expanding their networks, and a decent selection of mobile phones is now available that supports mmWave bands. Considering the potential for delivering gigabit speeds, 5G mmWave provides data over fixed wireless access (FWA) as an alternative to fiber to the home.
The critical challenge when operating at high frequencies is the limited coverage area and the dreaded dead zones. The physics of wireless signal propagation at mmWave frequencies are different than at low or mid-bands. To mention a few:
- Outdoors, signals do not reflect well around buildings or other obstructions such as signs and trees.
- Indoors, the situation is better due to the presence of many reflective materials that can create greater multi-path propagation;
- Building materials, such as brick, concrete, metal, and low-emissivity glass, limit outdoor to indoor signal penetration.
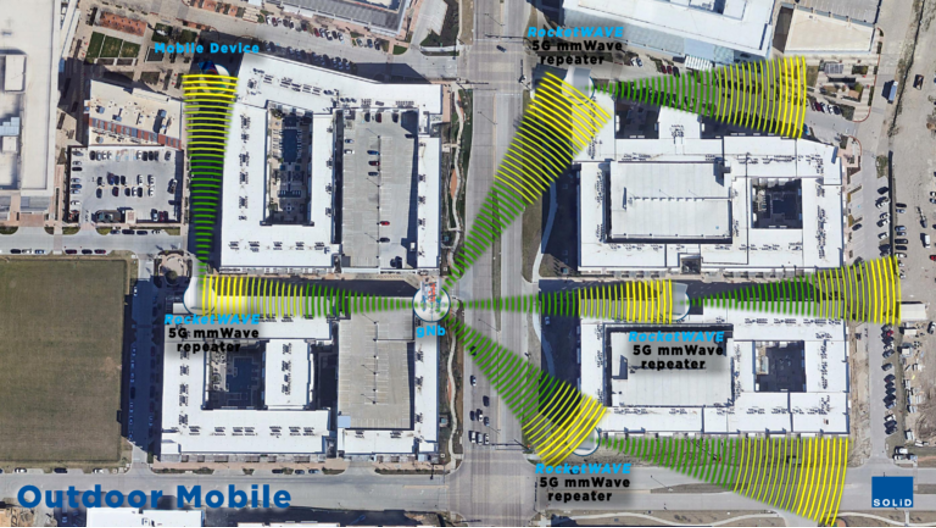
Outdoor coverage may improve by installing more base stations or small cells – but at a high cost, as each site requires a fiber optic connection for fronthaul/backhaul. Laying fiber cables in a city is expensive and a lengthy process that requires permits and digging up the ground.
Improving signal coverage with 5G mmWave distributed repeaters
Beamforming and beam refining features of mmWave repeaters digitally direct its receiver to the base station transmitter. The repeater receives the wireless signal over the air, reshapes, and retransmits a stronger signal in the desired direction to devices experiencing a coverage gap.
5G mmWave antennas may incorporate many antenna elements at its transmitter and receiver, which provide flexibility to shape the beam in the desired direction to improve the signal’s quality. Therefore, signal strength is no longer a static metric but rather more dynamic with adaptive antenna arrays.
Use cases for 5G mmWave repeaters
There are three primary use-cases for enhancing coverage with 5G mmWave repeaters: outdoor urban mobile, in-building mobile, and fixed-wireless access:
- Outdoor urban mobile coverage: repeaters extend coverage distance and retransmit signals around obstructions, which reduces CAPEX by decreasing the required number of 5G cell sites;
- In-building mobile coverage: mmWave signals do not penetrate buildings, so an outside-in macro-cellular approach is not practical. A rooftop or wall mounted repeater can feed repeaters located inside the building;
- Fixed wireless access: Signal strength often degrades quickly without line-of-sight from the building to the base station. Repeaters extend line-of-sight conditions and overcome the coverage gaps by intelligently repeating signals around obstructions such as foliage, buildings, and natural terrain.
Learn more about 5G mmWave coverage
This video interview with iGR explains how wireless coverage is different at 5G mmWave frequencies and how SOLiD’s RocketWAVE 5G mmWave repeaters can extend coverage to eliminate dead zones.
SOLiD DAS Keeps NYC Connected in Demanding Environments
https://youtu.be/Yr9J8C69XQY
The urban landscape of New York City is one of the most concentrated in the world. It includes soaring skyscrapers along with a vast maze of subway routes and road tunnels.
Everywhere in the city, visitors, residents and workers access wireless systems as never before. A June 2019 report from Pew Research notes that 81 percent of Americans have smartphones, up from 35 percent in 2011. Almost three-quarters own laptop or desktop computers, and about half own tablets. The proliferation of streaming HD video and expanding LTE and 5G services ensure a key role for distributed antenna systems (DAS) well into the future.
SOLiD DAS addresses wireless connectivity issues in demanding urban environments. Subways, tunnels and airports are some examples. Office buildings, condominium high-rises and other densely populated structures also need state-of-the-art equipment to meet both coverage and capacity requirements.
Evolution of Wireless Coverage in NYC
When Bandwidth Logic CEO Mark Parr spoke with SOLiD SVP of Operations Scott Deweese at Connect (X), they discussed the evolution of DAS deployments in NYC. Check out the full discussion here.
In the early 2000s, Bandwidth Logic deployed outdoor networks in Central Park. The company also set up networks for corporate clients like Pfizer and the News Corporation of America. Early contracts focused on pole top antennas and fiber installation.
Eventually, Transit Wireless was specifically created to deliver wireless services in the MTA subway. Ultimately, Transit Wireless chose SOLiD DAS to meet the unique demands of the subway environment. SOLiD’s equipment had already proven itself in the subway system in Seoul, South Korea.
Over the years, there’s been a change in who owns the equipment. The carrier consortiums of the early 2000s are giving way to third-party ownership of multi-carrier equipment. Bandwidth Logic is a third-party owner (3PO) dedicated to serving enterprises and carriers alike.
SOLiD DAS in NYC
In NYC, SOLiD DAS now enables 2 billion wireless connections annually.
Equipment versatility and durability are key factors in SOLiD’s success. For example, SOLiD’s Alliance DAS meets the demand for LTE services in any band. Alliance DAS can lock in radio frequency (RF) power levels to meet public safety communications requirements pertaining to 2-way (UHF/VHF) and public-safety (700/800) services.
SOLiD’s durable equipment performs well in demanding environments. For example, in the subway, heat exchangers on the subway cars emit heat throughout the system. Officials carefully examine proposed equipment to confirm that it will hold up in such a hostile environment. Everything must meet stringent standards, right down to the paint chip samples.
SOLiD: Subway DAS
The sprawling Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) subway system requires wireless coverage in 472 stations serving 1.7 billion riders/year. SOLiD leveraged its experience with other large subway systems to propose equipment for NYC's subway.
SOLiD’s success with the MTA subway led to yet another deployment in Toronto. SOLiD’s Alliance Multi-Carrier DAS is now in the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) subway system.
SOLiD: Airport DAS
NYC’s three international airports also need state-of-the-art DAS to meet demand. JFK’s six terminals serve 60 million passengers/year. LaGuardia’s four terminals serve 30 million passengers/year. At Newark International, there are three terminals serving another 30 million passengers/year.
SOLiD: Tunnel DAS
The three tubes that comprise the Lincoln Tunnel span 8,000 feet. They serve 35 million vehicles/yr. The two tubes of the Holland Tunnel cover another 8,100 feet. They serve 25 million vehicles/yr. DAS delivers vital wireless coverage in these unique environments.
SOLiD: Building DAS
Consider the magnitude of the DAS requirements in the city’s ubiquitous skyscrapers. For example, at the UN headquarters, SOLiD DAS helps to address the wireless needs of representatives from 193 countries. It also serves 1 million visitors/yr.
SOLiD’s state-of-the-art DAS is also critical in the 2.2 million sqft Empire State Building. This iconic attraction hosts 3.5 million visitors/yr. Residential structures have massive wireless requirements as well. Consider 432 Park Avenue, the tallest residential building in the world. The 412,637 sqft structure is 1,396-ft tall.
About SOLiD
Appearing across the depths of NYC’s dense urban canyons are wireless connection challenges aplenty. State-of-the-art, multi-carrier DAS is often the perfect antidote to what ails urban wireless communications.
Whether you’re a visitor, worker or resident in NYC, you already rely on SOLiD DAS to stay connected. In dense and demanding urban environments, wireless coverage and capacity requirements continue to evolve. As demands grow, SOLiD stands ready to deliver effective, durable DAS solutions.
SOLiD has been an innovator in wireless communications equipment for more than 20 years. For further assistance, please contact us today.
How Will 5G Impact Your Building or Venue?

“Is Your Property Ready for 5G?" is a webinar presented by Building Design + Construction. In the webinar, executives from SOLiD and Boingo discuss the opportunities presented by in-building 5G systems. Ken Sandfeld is President of SOLiD Americas. Doug Lodder is the SVP of Business Development for Boingo Wireless.
The Challenge
5G’s arrival is well-timed. The demand for wireless capacity is exploding. Cisco estimates mobile data traffic will increase sevenfold by 2022. In 2002, global internet traffic was about 100 GB per second. By 2022, Cisco projects that figure will be 1,500 times higher.
Many things will drive demand for increased indoor wireless capacity. Everything in your building, including IoT, is going to be connected to your wireless solution. This includes everything from building automation systems to smart door locks.
The 5G Response
You’ll want to develop a wireless system ready for the onslaught of growing demand. 5G delivers unprecedented capacity and speed. Its low latency will drive new wireless applications including IoT.
As individuals encounter 5G elsewhere, expectations will increase at your venue. Tenants, employees and visitors will want seamless delivery regardless of their data needs.
It's wise to develop the right wireless infrastructure to meet expectations. It's good to know that you may very well increase property values in the process.
State-of-the-Art Experience
In the webinar, Fodder asserts, “We’re really excited about what’s happening in the ecosystem of connectivity.” Properties that use emerging technologies to deliver a state-of-the-art wireless experience will stand out. An advanced infrastructure can:
- Drive operational efficiencies
- Attract higher rents
- Increase user satisfaction
- Increase property values
Long-term success depends on scalability and ready access to open technology.
5G Deployments By Property Segment
There’s a relentless focus on ROI in most commercial projects. There are many ways that 5G delivers excellent ROI. Sandfeld notes that SOLiD develops equipment with 5G in mind. He further asserts, “We’re able to expand our solutions to support 5G.”
Requirements for successful 5G deployments vary by property segment. There are differences in the need for wireless capacity in office venues, retail buildings and multi-family developments.
Office venues
It is possible to reduce initial costs by purchasing an infrastructure that starts small. But, it needs to be scalable as the system proves itself.
Focus on higher radio frequencies in office structures. This allows for smaller and flatter antennas which are easier to disguise. Lodder notes that the antennas are almost imperceptible at the Oculus, the transportation hub at the World Trade Center. Also, effective in-building wireless connectivity does not require bulky coaxial cables. Installers pull relatively small bundles of copper and fiber.
Retail buildings
When you calculate the cost of 5G upgrades, consider the cost of not upgrading as well. Fodder says “Be smart” to keep costs down. One way to reduce costs long-term is to make sure your wireless infrastructure is eminently scalable.
Fortunately, in both retail and office settings, retrofits don’t always require that you start from scratch. At many venues, modern systems use lightweight cabling and equipment that facilitate the process
Multi-family developments
Developments that offer superior wireless connectivity can command higher rents. Tenants value the convenience inherent in a state-of-the-art system. It may enhance occupancy rates as well. Owners benefit from common area security and conveniences enhanced by advanced systems.
Important Role for CBRS
As of 2018, Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) became a viable in-building wireless option. When it comes to commercial venues, Sandfeld says, “CBRS is an amazing opportunity for building owners.”
CBRS offers key advantages. First, it addresses the limitations posed by carrier licenses. With traditional licensing arrangements, whoever controlled the license controlled the spectrum. By contrast, CBRS-based LTE solutions support all four carriers: Verizon, T-Mobile, Sprint and ATT. They will support future operators as well. Second, it delivers attractive economics for mobile coverage/capacity. Third, the wide 150 MHz shared spectrum delivers 1.5-gigabit theoretical 5G speeds. CBRS will allow for “dedicated lanes” devoted to specialized needs. Fourth, a CBRS-based system gives venue owners access to valuable data analytics.
CBRS systems are already becoming a reality. For example, Fodder notes that Boingo has deployed an early version at Love Field in Dallas.
Proper Planning
Sandfeld notes how important it is that cable installation occurs as the building goes up. Most commercial developments have protracted timelines. Stakeholders should include wireless connectivity in deliberations from Day One. For example, seek input from the engineers about the physics of radio frequency needs.
With proper planning, you’ll end up with the wireless infrastructure you need to deliver services tenants value.
About SOLiD
SOLID has been providing in-building wireless solutions for 20 years. Today, the company is poised to contribute to the 5G era. In fact, some of the world’s very first 5G networks are deployed on SOLiD equipment in South Korea.
SOLiD’s wireless solutions enhance wireless communications at many high-profile sites. Examples include international airports, major sports venues, leading hospitals, prestigious universities and Fortune 500 corporate campuses.
To access the webinar, “Is Your Property Ready for 5G?”, visit SOLiD.
Active Vs Passive DAS Systems

Public safety officials understand how vital in-building wireless connectivity is during an emergency. There are numerous sobering reminders of the extreme conditions under which emergency responders must often perform their duties. Effective, uninterrupted communication is always vital.
As a result, Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJs) require state-of-the-art radio communication systems for emergency responders. Public safety distributed antenna systems (DAS) often address such needs. They are deployed in new construction and existing structures.
Factors Impacting Public Safety DAS Design
Designers of public safety DAS systems face complexities that are uncommon in commercial DAS. The uplink design is especially crucial. The lack of power control on portable radios is an important factor. DAS system designers must always consider the performance and capabilities of all active equipment in use.
Key factors influencing the design of a public safety DAS include venue size, required frequencies, signal strength, coverage and local codes.
Venue size
Usually, the size of the venue determines whether an active or passive DAS solution is most appropriate. Typically, passive DAS systems are limited to structures with up to 500,000 sqft of space.
Frequencies
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) regulations guide many AHJs. NFPA 72 includes rigorous requirements for a public safety DAS that commercial DAS does not face. It must operate on frequencies designated exclusively for first responders only.
Signal strength
Systems must deliver an inbound signal strength of at least -95dBm. The same strength is required for outbound signals at the donor site. Note that certain AHJs may require different minimum signal strengths.
Sec. 24.5.2.2.3 of NFPA 72 requires a public safety DAS (with FCC-certified signal booster), radiating cable system or other approved system when the required signal strength is not otherwise attainable.
Coverage
While a commercial DAS focuses only on areas where people are regularly present, a public safety DAS must provide coverage in stairwells, basements and other lesser used areas as well. Finally, there must be back up service to ensure continuous communication the event of an outage.
General building areas require 90 percent floor area radio coverage, while certain specific areas require higher levels of coverage. For example, Sec. 24.5.2.2.1 of NFPA 72 requires 99 percent floor area coverage in all areas defined as critical by the AHJ. Examples include fire command centers, fire pump rooms, elevator lobbies, exit stairways and standpipe cabinets.
Local codes
Public safety DAS must also comply with the local codes that vary from region to region. Although NFPA and IFC provide a framework for these regulations, they do vary. Some AHJs have their own specific requirements. Ultimately, it is necessary to follow local code requirements set forth by the AHJ with jurisdiction.
Difference Between Active vs. Passive DAS Systems
Commercial DAS systems enhance worker productivity, improve visitor experience and increase property values. The goals of public safety DAS systems are quite different. They speak to the needs of emergency responders when a communication failure is not an option.
Systems must overcome structural communication barriers like concrete and low E-glass. Other active DAS systems are deployed to increase network capacities to meet expanding mobile data requirements.
Active DAS Systems
Active DAS systems deploy fiber optics, remote antenna nodes and other components to enhance in-building wireless connectivity. Active DAS can improve both reliability and capacity. Active DAS solutions address needs for both increased reliability and capacity. Amplifying and distributing signals evenly throughout a building enhances reliability. System designers can provide as much capacity as is needed by breaking up the DAS into different zones, all fed from a common head-end location.
Passive DAS Systems
Passive DAS solutions rely primarily on signal boosters to deliver reliable in-building wireless connectivity. Unlike active systems, they only increase reliability, not capacity. They are considered passive systems because theyare distributed only through parts that don't require power such as splitters, coaxial cables and couplers. Passive DAS systems simply use donor antennas and BDAs (Bi-Directional Amplifiers) to boost the signals to and from the donor site.
Contact SOLiD Today
A properly designed public safety DAS is critical to the safety of first responders and those who require their professional assistance.
We’d welcome the opportunity to address your public safety wireless communication inquiry, whether you are an AHJ, a DAS system designer/integrator, a building contractor or an electrical contractor. SOLiD’s innovative, cutting-edge DAS solutions are deployed around the world. Let us put our knowledge and experience to work for you. For prompt, friendly assistance, please contact us today!
MWC19 Barcelona Predictions

What announcements or new initiatives are we likely to see at this year's MWC? Three key themes to watch for include O-RAN Alliance news, innovative 5G applications and the further development of private LTE solutions using CBRS.
O-RAN Alliance News
The O-RAN Alliance was announced at last year’s MWC, and it now includes most of the industry’s Tier 1 providers. At MWC19, look for major operators and suppliers to make significant O-RAN announcements.
The work of the O-RAN Alliance addresses important topics like Open Interfaces, Intelligent RAN Control, RAN Virtualization and White Box. O-RAN defines next-gen RAN architecture, enabling increased use of infrastructure virtualization and embedded intelligence.
Certain initiatives will likely address the rapidly evolving demands of the RAN marketplace, including:
- Simplified deployment
- New technology concepts
- Reduced costs
- Innovative business models
As the 5G era dawns, the open interface defined by the O-RAN Alliance will promote a more agile response to exponential increases in network complexity. Open APIs and interfaces will be further empowered by AI, heralding a new era of synchronicity.
O-RAN provides an additional point of entry to the market for vendors and industry innovators. SOLiD recently joined the O-RAN Alliance as a contributing member. The company is committed to delivering solutions to global operators based upon the protocols established by the O-RAN Alliance. Examples include Genesis DAS, IA-8000 and its mobile front-haul solutions.
5G Opportunities Multiply
As 5G deployments continue to appear on the horizon, its myriad practical applications will only be limited by the collective imagination of industry innovators.
Support of massive IoT
5G’s arrival is well-timed to address the demands of a rapidly expanding Internet of Things. Estimates of the number of in-service IoT devices range up to 50 billion by 2020. 5G responds with an exponential increase in capacity, seamlessly connecting these myriad, ubiquitous devices.
Reliable low-latency communication
5G’s low latency makes it attractive in the public safety space. It can also enhance smart-grid control, robotics, industrial automation, drone control and more.
Enhanced mobile broadband
5G will also deliver an exponential increase in power required to deliver real-time responsiveness in mobile broadband. For example, it can respond to the burgeoning needs of both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
LTE Networks and CBRS
Industry buzz about private LTE networks and use of the CBRS spectrum will drive numerous conversations at MWC19. CBRS spectrum access will supercharge the development of private LTE networks. For many enterprises, these private networks are attractive because they simultaneously address coverage, capacity, compliance and security needs.
Specifically, private LTE will enhance everything from IoT to enterprise connectivity. A CBRS field trial for first responders is underway in Clarksville, TN. The NFL may use CBRS to replace established two-way radio communications in stadiums. The PGA wants to use CBRS to address capacity issues that occur when thousands of fans arrive for golf tournaments.
It is likely that vendors will launch CBRS-capable smartphones and other devices at this year's MWC. End-to-end system testing expanded in 2018, as numerous vendors and operators worked to fine-tune CBRS use. For example, on April 5, 2018, Verizon announced a collaborative effort to expand LTE networks across the CBRS spectrum.
About SOLiD
SOLiD (https://www.solid.com) drives extreme edge connectivity through a portfolio of DAS, optical and IOT solutions to connect people, places and things in a fantastically connected world. SOLiD delivers distributed antenna systems, optical transport and IOT solutions across the globe. SOLiD enables indoor and outdoor cellular and public-safety communications at some of the world’s best-known and most challenging venues including leading hospitals; professional, and college sports venues; government, university and Fortune 500 corporate buildings and campuses; international airports and metropolitan subways; industrial and logistical facilities; and other high-profile sites.
For further information on SOLiD DAS, Backhaul and Fronthaul and IOT solutions go to www.solid.com or call 888-409-9997
What’s Up with Private LTE Networks? Part One

First of a Two-Part Blog Series
There’s much talk in the wireless industry today about private LTE networks. Some of these questions include: are these networks dependent on 5G? When are the private networks coming? What technologies will be adopted? Where will they develop first?
Many see the evolution of the private LTE network as an exciting, and important implementation of in-building wireless solutions . I do too.
Looking into the future as additional frequency bands are introduced to the market on which these private LTE dependent, we can easily envision a rapid proliferation of applications, devices, and use cases unleashing an incredible amount of value, particularly related to private LTE deployments.
These days I am hearing about private LTE at wireless conferences and in customer meetings from those considering the range of in-building additional wireless solutions public LTE, private LTE and WiFi.
But recently, what has surprised me is that I’m hearing from customers, particularly those in the commercial real estate, hotel and healthcare markets who are inquiring about private LTE networks and how they may suit their businesses. Many are now asking about CBRS technology, and its potential impact. In this article, I am not going to discuss what is CBRS and all its concerns (timing of CBRS approval by the FCC, rollout of handsets, etc …) but will rather focus on the business drivers for a private LTE network.
Benefits of a Private LTE Network
A private LTE network is one which an enterprise deploys LTE technology exclusive to their enterprise to meet mobility, communication and automation needs within their physical and vital walls. The network can be operated by the enterprise or by a third party. This network is not dependent on 5G technology, but can be built in the very near future on existing LTE technology.
There’s been a fair amount written about the benefits of a private LTE network including coverage and capacity, and customer design/configuration for specifics environments. Those two benefits are important reasons to consider a private LTE network, but I’d like to suggest two additional benefits.
First, is security. The second, is compliance. So, let’s add those two to the list and let’s explore some industries.
Commercial Real Estate
Commercial real estate executives look to keep tenants happy, their buildings full and keep costs in check. One example might be the experience of a financial services firm, such as a brokerage firm who is leasing space in a new building. It’s critical that the communications infrastructure meet the demands of the brokerage firm. How might private LTE be implemented in this example?
Security- This is where the financial services can really benefit with a private network to provide enhanced, and controlled voice and data security.
Compliance- For example, in cases where voice authorization is needed, and recorded, a private LTE network can provide for voice recording in a quick, seamless and compliant way.
Coverage and capacity– In addition to their desk phone number, nearly all brokers provide their cell phone number to clients as the primary way to communicate. It’s simply a matter of fact that in-building wireless is ubiquitous and clear, since each communication is of potentially high value, and is critical to any transaction. Superb in-building wireless is required.
Designed for specific environment- New buildings can provide a challenging coverage and capacity challenge. A private LTE network can be controlled to meet those demands.
In the next part of this series, we'll explore the benefits of private LTE network in industries such as healthcare and hospitality.
Evolution of 5G Indoor Wireless Coverage

Evolution of 5G Indoor Wireless Coverage
The much-anticipated arrival of 5G indoor wireless promises cutting-edge performance even as internet-reliant devices proliferate in the workplace and beyond. Wireless operators, wireless design engineers, telecom distributors and others in the industry stand ready to take on the challenges of 5G deployment to realize exponential increases in performance.
New Technology Outpaces the Old
Despite common perceptions, 5G is not just a new and better version of 4G. To better understand the radical difference between the two, consider this automotive comparison. When U.S. News rated the 25 fastest sedans for 2018, there were some impressive entries. For example, the $205,000 Bentley Flying Spur hits 60 mph from a standing start in 4.3 seconds, good for 22nd place.
Although sports performance leaders like BMW, Audi, Jaguar and Mercedes placed many gas-powered cars on the list, an electric vehicle ranked first. The 0-60 time of the 2018 Tesla Model S P100D was 2.3 seconds, a full half-second faster than its nearest rival, an eternity in automotive acceleration.
Eye-popping Performance
Think of 5G as that top-rated car that blows away the competition with new technology. Just as electric propulsion delivers eye-popping acceleration, so too does 5G deliver ultrafast downloads. Whether it’s a speeding car or streaming data, you want to get from Point A to Point B as fast as possible. Just as high-torque electric vehicles deliver eye-popping 0-60 times, 5G races out ahead of 4G with ultrafast download speeds.
As LifeWire says, “One fundamental difference is 5G’s use of unique radio frequencies to achieve what 4G networks cannot.” Just as EVs use a different power source, so too does 5G use different radio frequencies.
To more fully understand the differences between previous generations of wireless communication and 5G, take a look at this comparison chart prepared by RF Wireless World. We’ve come a long way since the 10 Kps voice and data transfer maximums of the 2G era. While 4G data transfer capacity reaches 1 Gps, 5G delivers 10-20 times that amount. Where wireless data once traveled the veritable cobblestone streets of telecommunications, 5G promises hyperloop-level speed.
Ultra-fast Wireless Solutions
In-building 5G requires more and smaller antennas to deliver precise directional control of ultrafast data delivered with minimal latency.
What does this mean in the real world? Where 4G delivers data quickly, 5G delivers it almost instantaneously. Visitors throughout your building will enjoy a better user experience. You may see more productivity from workers who regularly download videos. Those who use Skype or FaceTime will now enjoy a smoother, more realistic experience. Performance gains are impressive. According to LifeWire, “5G will support over 1,000 more devices per meter than what’s supported by 4G.”
The new technology benefits from the use of frequencies that can accommodate the higher bandwidths required for 5G performance. However, 5G is by no means a monolithic technology. Rather, it delivers different solutions using millimeter wave bands and sub-6 GHz, with every band having its own method of implementation. For example, sub-6 GHz solutions tend to parallel today’s 4G solutions. By contrast, millimeter wave solutions will initially share 4G in-building infrastructure before they evolve over time. Those that deliver in-building wireless solutions must continually innovate to more fully exploit 5G’s unique characteristics.
In the future, even as internet-dependent devices require larger and larger downloads, your building’s 5G network will be able to cope.
Learn More
SOLiD provides advanced in-building wireless solutions for diverse venues, including office structures, hospitality, commercial real estate, healthcare, academia, entertainment venues and transit centers.
Our full-service, comprehensive approach includes engineering & design, monitoring & maintenance and training & certification. For prompt, professional assistance, please contact us today.